Research
The research of the project Virtual Acoustic Space is mainly carried out in two slopes. On the one hand, from the Department of Physiology of the University of La Laguna, studies are carried out on neurophysiologic aspects of the perception of sound, perception of phospenes and neuropsychological evaluation of the people who have offered themselves as volunteers for the experiments. On the other hand, in the IAC's Instrumentation Area studies are carried out on systems of depths maps calculation using stereovision, perception of sounds, signal processing techniques and HRTF functions measurements.
Ssome of these fields of investigation are summarized below. For a more detailed information, see Documentation.
Neurophysiologic Aspects.
The mental representation of the world on the brain can be independent, up to a point, of the sensorial route by which the information arrives, as far as this one is suitably received and recognized by the brain.
In this sense, a common neurophysiologic substrate to the different modalities can occur, where a processing would be made that has occurred in calling amodal or supramodal. Are of interest the neurophysiologic studies that are being made with the modern techniques of they neuroimagen, well-known like Functional Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (IMRf) and Transcraneal Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) to locate, if they exist, the areas implied in the perception of figures in auditory surroundings and to be able to thus establish comparisons with the tie areas to similar perceptions on the part of other sensorial modalities.
At this moment we shuffled three hypotheses, that they are not excluding to each other, with respect to the nature of the neurophysiologic substrate of the auditory space perception:
1.- That it is constituted by areas of multisensorial processing.
2.- That areas that take part in the visual function collect and process the information giving an exit similar to which they give before the own one via line of vision.
3.- That silent areas of the auditory system sphere activate previously.
Given to the nature and complexity of the human nervous system, the only ethical possibility of its study is the use of noninvasive techniques (nontraumatic), within which the most used they are the corticoencephalography and nuclear magnetic resonance of functional character, both available ones in our group. In this project we try to study the plastic changes that take place after the continued use of the developed system, as well as to evaluate some of its possible applications in bioengineering of the sensorial substitution from our capacity of confirm, through fMRI, the activation of certain cortical zones of visual processing during the generation of acoustic scenes of different degree of complexity. This confirmation, along with the opportune line of investigation, if there were place for it, could be as well of relevance as far as a utility of the system not only in the daily life of the blind person, but also in the ample field of the sensorial and psychomotor rehabilitation, in special in the area of the space perception, direction and mobility.
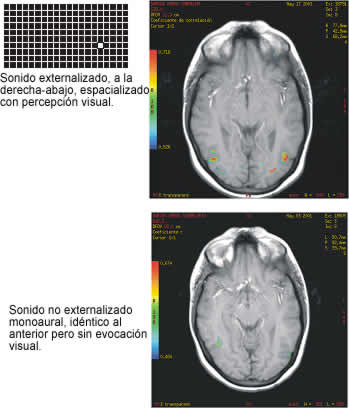
(More examples of images of brain's cross sections whith submission to sonorous stimulus, in different cases, and with phosphenes evocation, here)
We arrange of a system to make studies of functional magnetic resonance of 1.5T, model Horizon Sigma hiSpeed, of General Electric, equipped with programs to fMRI "FUNCTOOL".
Phosphenes perception.
As a proof of the important implications of the confirmation of one or another one of the previous hypotheses, we described one of the found phenomena briefly, the one of the perception of lights evoked by sounds: Some of the blind people and also not blind people refer to perceive in the point where they locate a sonorous source auditorily, flares (described as small lights or stars), simultaneous with the auditory perception and induced by this one. This phenomenon, with some but little antecedents in literature, is known like phosphenes induced or evoked by sounds, although it emphasizes its clear space location here and the possibility of controlled generation or induction. It seems to depend on as much individual factors as of the nature of the used stimulus and is being object of study as far as its nature, neurological substrate and conditions of appearance.
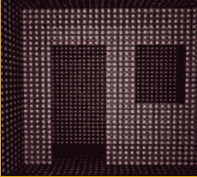
Visual representation of the image of a room by a blind person using our prototype. Each luminous point would represent a phosphene.
Neuropsychologic Evaluation.
The team of psychologists who take part in this project tries to tend a bridge that puts in contact the EAV technology with the necessities and individual characteristics of the blind people who are going to make use of the same one.
The use of the prototype demands of the brain the accomplishment of a task to which he is not customary, requiring the anatomical-functional reorganization of the implied cortical areas. From this fact two questions are come off that our psychologists try to solve: on the one hand, the necessity becomes evident of the implementation of a training system for the blind people where it becomes qualified the person to extract of the prototype the maximum of possible information, guiding the people in its process of acquisition of these new cognitives abilities. From this necessity arises the question of how it must be that process of training, how it must be the approach of the people to the prototype, that is to say, the presentation of the information has to be massive and to leave the person to find, with time and the practice, the clues for the interpretation of the information provided by the prototype, or, the information has to be progressive, learning first to discriminate simple parameters like the distance, the size or the direction of individual form for, later, being grouping those different aspects in the perception from a complex environment?
In addition, it is tried to diminish the duration of the sessions and to establish the suitable temporary space among them, in order to diminish the possible negative effects (anxiety, headaches, fatigue, frustration, etc.) that they could be come off this process of learning.
After the training with the prototype, some neuropsychological tests of intellectual yield, etc. are made to try to not only discern if the use of the prototype affects and how to the yield in these tests, but also if the intellectual yield predicts the success in the training or affects the way in which the same one must be developed. One of the profits of our group of psychologists is the adaptation of these tests for the blind community.
Capture System By Means Of Stereovision.
Our line of investigation in this field is focused towards the attainment of a system that is able to acquire the distance to the objects of the frontal field through two small microcameras placed in a support adapted to the height of the eyes. From the obtained images the depths map is calculated: the information of three-dimensional position of each one of the points, within a certain level of resolution, of the surface of the objects located within the field of view. A sound is associated to each calculated position so that, sent through earpieces to the person, it gives the impression to him that it comes from that specific space position. Thus, the set of visual positions calculated for a scene is sent, image to image, in form of a set of auditory positions, being created the illusion from which the sounds seem to come from that digitized surface of the objects.
Space perception of the Sounds and HRTF Functions.
Regarding the space aspects of the auditory perception, the bigger amount of the research has been centered in the study of the capacity of sounds localization. A series of fundamental cues in the sound information that arrives at the ears has been identified therefore from which depends the awarding on a position in the space as origin of the sound, in particularl: the interaural differences of time and intensity whereupon arrive the sound at one or another ear based on their position and sonorous intensity and the content in reverberation from the sound, that take part in the distance perception. The signal that reaches each eardrum is modified with respect to the signal that left from the emitting sonorous source by the acoustic action of the structures of the head and the trunk, in special by the auricular pavilion in each side. This one determines, with its particular form and its creases, that determined frequencies of which compose the sound are amplified as opposed to which they are attenuated. These modifications are dependent and largely specific of the position of origin of the sound. This effect dependent direction can be extracted in form of a mathematical filter that characterizes it and that recognizes with the terms of Head Related Transfer Function (functions HRTF). The pair of filters for each ear corresponding to a certain position in fact contains all the mentioned clues of information of space interest. Independently of the real space origin of the sound, in the measurement in which this sound reaches to both eardrums taking printed all the physical characteristics determined by the place of origin of the same one in relation to the person, it will be possible to have a suitable perception from where that sound comes.
A system for obtaining these filters has been developed, so that a pair of filters for each position of the space recovers that is wanted to simulate. Since the anthropomorphic characteristics of the different individuals are peculiar and different, to obtain most correct transference functions as possible, it has been chosen from a beginning to measure the set of own HRTFs of each individual.
At the moment we are investigating different techniques so that the measurement of HRTF functions will be fastest, more effective and more comfortable for the user. We are considering technics like the one of mathematical interpolation to reach more resolution, to reproduce the external auditory pavilion of each individual by sculpturic techniques to make the measures on a dummy or, when a great number of measured HRTF functions exists, to secrete these functions in dependent groups of some parameter of easy measurement in the people, so that we could assign a HRTF function to each user from a bookstore of functions that we have stored.
Monosource, Bisource and Multisource Experiments.
These three experiments, by chronological order, are those that have been carried out in the equipped room of the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands. Here you can find a detailed description of each one.
HRTF Functions Measurements.
Here is an explanation of the HRTF functions measurement test that we did 8th November 2002. This explanation can give you an idea of how we measured this so important parameter for our investigation.
Pixelization Experiment.
With this experiment we try to measure the amount of visual information that we need to be able to develop in our surroundings. The obtained results have direct application in the EAV project. You you can find more information here.



Home | Summary | History | Instituciones | People | Research | Development | Documentation | Patent | Multimedia | News | FAQs